How does static electricity arise?
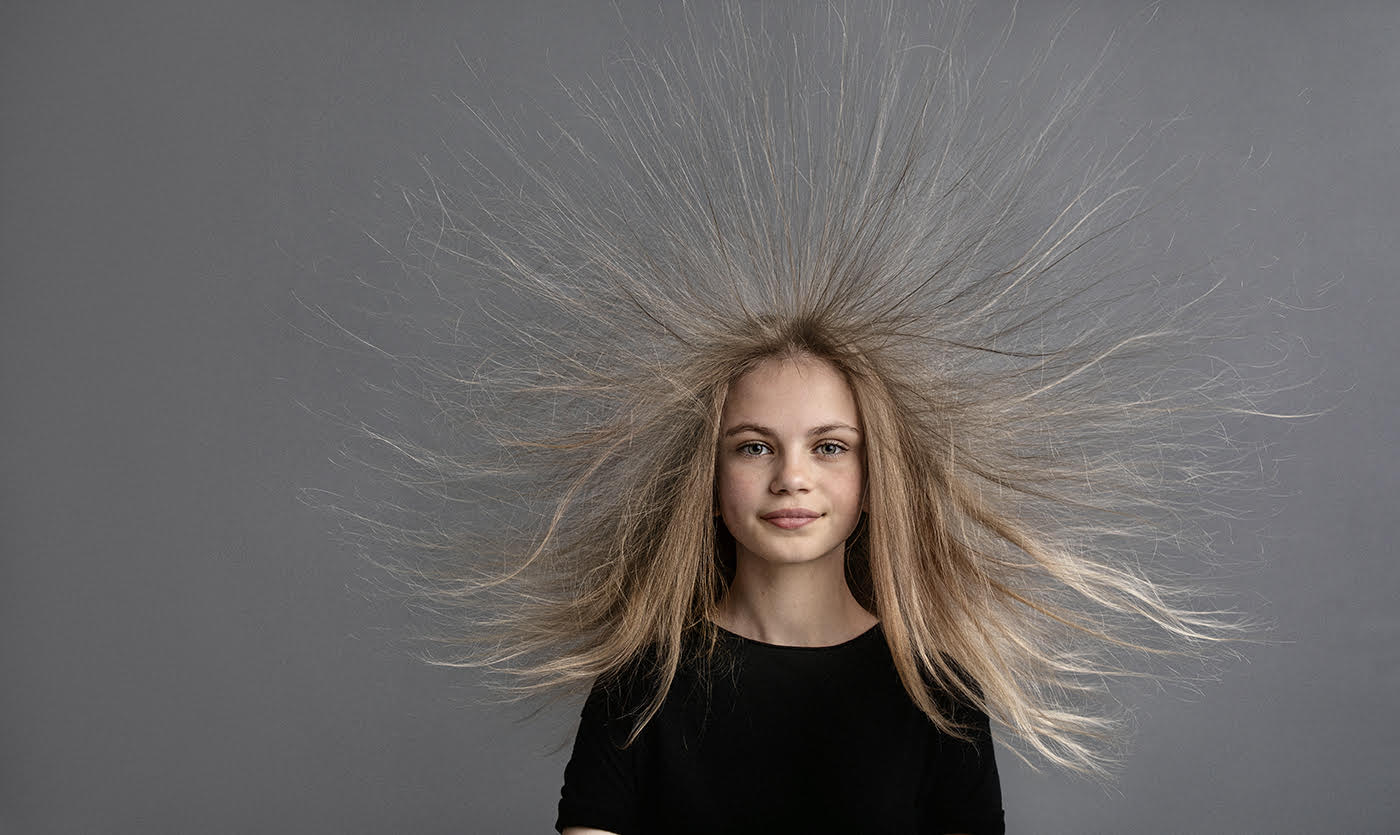
What causes static? My hair always gets static in the winter. How does static electricity happen, and why is it worst in the winter?
Things become static when they give off or receive electrons from other materials, which makes them electrically charged. For example, hair gets a positive charge when you pull a wool sweater over your head, because the hair gives off electrons.
Positive charges repel each other, causing your hairs to stand apart to avoid each other. Your hands always give off electrons when you touch something. That's why you get a shock when you open a car door, for example, because electrons from the door jump to your hand.
Humid air reduces static electricity
Materials are capable of releasing electrons to varying degrees. If you pass glass with a woolen sweater, the sweater receives electrons from the glass and is negatively charged. But if you iron the sweater along polyester or plastic, the sweater gives off electrons and is positively charged.
Water conducts electrons well, and therefore there is less static electricity when there is a lot of moisture in the air. In winter, humidity is often low, so things become static faster.

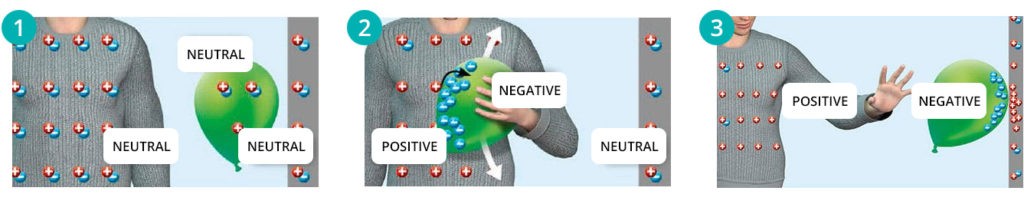
This is how static electricity is created
1: Some materials, such as wool and plastic, easily lose or receive electrons, making the material static.
2: A balloon and a woolen sweater iron along each other. The plastic steals electrons from the wool, and the balloon is charged negatively while the sweater gets a positive charge.
3: The excess electrons on the surface of the balloon repel electrons on the wall. The positive particles - protons - in the material of the wall attract the balloon, because positive and negative attract each other.
Preventing static electricity
Do you suffer a lot of static electricity in the winter? Then consider using a humidifier to increase the humidity in your home, this will make the electrons conduct less well.
-
Beam BlackOriginal price was: €189.99.€89,99Current price is: €89.99.
-
Ovi€99,99